Acne: Definition, Causes, Complications and Treatment
Introduction
Acne is a chronic skin disease of hair follicles of the face, chest, neck, shoulders, and back occurs commonly in all teenagers and in some adults during their puberty period. It causes pimples, blackheads, and scars, but not serious. Our skin has tiny pores, which can be occluded by dirt, oil, dead skin cells and bacteria. When this happens pimples or zit may develop on the skin. Repetitions of pore obstruction on the skin may lead to acne. It begins when the oily substance from the sebaceous glands (oil gland) under the skin blocks the tiny openings of the hair follicles.
Acne Types
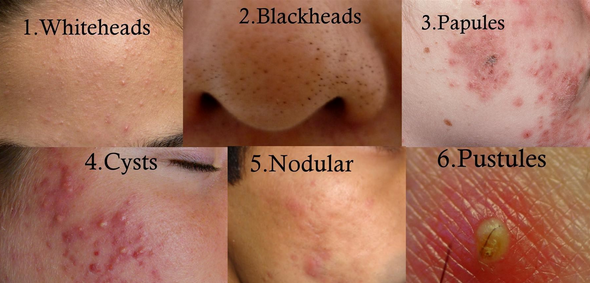
Acne can appear in several types (acne types).
- Blackheads: If the pore size is larger then the clog appears as blackheads, a small flat spot with its centers as dark in color. In this type, pimples rise on the surface and are non-inflammatory.
- Whiteheads: If the pore size too small then the clog appears in the form of whiteheads. This type of a pimple stay under the skin surface and this type is also non-inflammatory acne.
- Cysts: It is a deep, white pus-filled centers and painful pimple which results in scar and red lesions.
- Nodules: It is an inflammatory, large, and firm pimple deep within the skin having a half centimeters in its diameter. This type of a pimple makes painful lesions and scar.
- Papules: Small and tender bumps, which is pink in color and elevated on the skin.
- Pustules: Small inflammatory blister which is pus-filled and is elevated on the skin.
History
In the mid-5th to mid-6th century, ancient Greece, the earliest description of pimples seemed inside the writings of the Byzantine physician Aetius Amidenus.
The word pimples seem to have developed from the Greek phrase acme, this means that "point or spot." from the historical facts, each Hippocrates (460–370 B.C) and Aristotle (384–322 B.C) were aware of this illness.
Until the 1800s, humans did not find out any extra useful remedies against zits and have constantly used sulfur due to the fact they noticed it can dry and exfoliate the skin.
1920's – Benzoyl Peroxide is used
1930's – Laxatives were used to cure for 'chastity pimples'
1950's – When antibiotics were discovered, they had found beneficial effects on acne. Initially, it was administered orally.
1960's – Tretinoin (Retin A) was found to be effective for acne. This paved the way to develop oral isotretinoin (Accutane and Roaccutane) since the early 1980s.
1980's – Accutane is established in America
1990's – Laser treatment was discovered
2000's – Blue/red light therapy was used
Occurrence
About 85% of human beings between the ages of 12 and 24 experience at least minor pimples. Globally, acne influences approximately 650 million human beings, or about nine.4% of the populace, as of 2010. It impacts almost 90% of human beings in western societies at some stage in their teenage years, however, can occur earlier than youth and might persist into adulthood. Whilst acne that first develops between them a long time of 21 and 25 is unusual, it impacts 54% of women and 40% of guys older than 25 years of age.
Causes
- Acne is caused by few problems that arise during the lubrication process in the skin. These artifacts can occur when:
- The largest amount of oil is secreted by hair follicles
- Accumulation of dead cells in the pores
- Bacteria occupy the pores in the skin
- When the dirt and bacteria are occluded in the pores, secreted oil is unable to come out thus a pimple or zit is formed over the pores.
- Acne also occurs when the sebaceous (oil) gland under hair follicles are stimulated during the puberty period and also because of other hormonal changes.
- When an inflammatory pus-filled cyst or blister ruptures, the fluid comes out and it spreads into the adjacent surfaces of skin. The bacteria and dirt in the pus cause the growth of another pimple adjacent to the existing pimples.
- The weakened immune system also plays a major role in invading of bacteria into the pores of the skin.
- Androgen is a male hormone, which regulates the secretion of oil in the sebaceous glands. Androgen levels are raised when the adolescence begins.
- Rising in levels of androgen causes the oil glands under the skin to grow larger. Thus the enlarged oil glands start to secrete more amount of sebum (oil). Excessive oil causes rupture of the cell walls in the pore and thereby bacteria invade easily into the pores.
- The family history of acne. When the parents are more prone to acne in their adolescence, then there are chances of getting acne to their offspring.
Risk factors
There are various risk factors leads to cause of acne:
- A medication that contains high androgen, barbiturates, corticosteroids, and lithium
- Birth control pills
- Cosmetics that are too much greasy
- Hormonal changes during mensuration in women
- Mental stress cannot cause acne but if you have acne earlier stress may make it worse
- A diet rich in refined sugars or carbs and oil
- Exposure to highly polluted environment
- Too much dandruff on the scalp
- Excessive washing of the face can dry and irritate the skin
- Occupation in industrial locations wherein exposure to halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons
- Use of dirty or rusted razors also at risk of developing acne
- Touching or pricking the pimples of other persons
- Friction, stress or pressure on the skin
- Age between 12 and 24
- Picking or squeezing the existing pimples or zits
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the severity of the acne condition:
- Blackheads (open pores that contain oil, when its exposed to air it turns into brown)
- Whiteheads (closed plugged pores)
- Cystic lesions (present under the surface of the skin, which is filled with pus and it is painful)
- Nodules ( Large, solid, painful lumps beneath the surface of the skin)
- Pimples (pustules) which are papules with pus in tips
- Small red, tender bumps (papules)
 |
| Whiteheads acne |
 |
| blackheads acne |
Complications of acne
Acne will get rid of as you get older. Scarring may happen if acne goes severe. It can be permanent, but over a long time, it can improve.
Scarring: One in five people with acne will get scarring. Scarring may increase due to picking squeezing or spots. Scars can be ice pick or broader pockmarks. First, it will be purple in color before it fades to a whitish color; sometimes 'keloid' (firmer lumpy) scars may develop on your skin.
Hyperpigmentation: It usually occurs in dark skin tone. Skin becomes darker in the affected area.
Physiological problems: Acne may create physiological problems such as anxiety or making you feel depressed. For example, if people commenting on your acne can affect your self-confidence. Talk to your general practitioner if you feel depressed or low.
Diagnosis and test
Mostly dermatologist can diagnose acne by examining the affected skin. Your doctor may ask several questions that are aimed at diagnosis of acne and to find out other skin disorders. Some of the questions include.
- Drug allergies, which faced before
- Use of steroids (e.g. body-building)
- Depression or mood swing
- Medications were taken for other diseases that may affect your skin that cause acne
- Eczema or area of sensitive skin
- Irregular menstrual periods in women, use of contraceptives, breastfeeding, and past or present pregnancy
In some other cases, acne can develop some other related skin disorders, such as rosacea. This information will be helpful for the doctor as an informed diagnosis.
Treatment and medications
The main goal of the treatment is to reduce or to eliminate the outbreaks and to prevent scarring. Your doctor may give treatment based on your severity of your condition. Initially, for some people, treatment may worsen your condition. Based on the condition, treatment should be given minimal for two to three months before deciding the treatment is effective.
There are varieties if excellent medications are available such as follows:
Benzoyl peroxide: It kills bacteria on the skin surface. It can be applied once or twice a day to work against pustules. It should not be used near eyes and mouth thought it will be irritating to those two areas. If it is used excessively, it causes dryness and redness of the skin.
Accutane (Isotretinoin): It is the most aggressive therapy for acne. It has severe side effects so it is reversed for severe cases that are resistant to other treatments. It mainly reduces oil production and it keeps gland clear by cell shedding.
Oral and topical antibiotics:
Doxycycline, Erythromycin, and Minocycline are commonly used antibiotics. It kills bacteria that cause inflammation and are useful when acne is inflamed and increased.
Retina A: It helps to clear glands and limits whiteheads and blackheads from evolving.
Prevention
- Daily wash your face twice a day with an oil-free and water-based cleanser. Avoid vigorous washing that worsens acne and it damages skin surface
- Don't squeeze or pick pimples because that may cause skin scar, swelling or it may worsen the acne
- The common side effects of acne are skin peeling and dryness. This can be prevented by using moisturizer
- Keep your hair clean and prevent it from touching the face and hands
- Wash your sheets once a week because sweat and dirt are on sheets may cause acne development
- Wear loose clothes to prevent sweating that may cause skin breakouts
- Use products that labeled as water-based or non-noncomedogenic
- Many acne treatments increase sensitivity towards sunlight, so wear fully closed cloths or sunscreen lotions
You Might Also Like:




.webp)






No comments: