GIFMIS: The Ghana Integrated Financial Management Information System
1. Introduction
Ghana Integrated Financial Management Information System (GIFMIS) was launched in May 2009 to succeed the Budget and Public Expenditure Management System (BPEMS) Project, which ran from 1999 to 2008. The project was to be the fourth component of the e-Ghana Initiative, with a pooled donor money of US$ 120.52 million.2. Goals
The GIFMIS project's aims were as follows:- Promote competence, clarity, and accountability in public finance management via sound reasoning and transformation of the Ghanaian government's budgeting and public spending management (GoG).
- Promote proper information dissemination for financial management.
- Appropriate Administrative Decrees and Regulations in the financial sector.
- Enhance revenue collection techniques and procedures.
- Increase payment and commitment control efficiency.
3. Justification (disadvantages of previous systems)
The previous system, BPEMS, had a number of shortcomings, which served as the impetus for the development of GIFMIS. These downsides or defects included the following:- Difficulty acquiring accurate and timely data on budget allocations, commitments, and actual income and expenditures.
- Delays in the payment and financial reporting processes.
- Corrupted information flow for evaluating budget performance.
- Inconsistent Charts of Accounts (COA), which makes comparing budget performance difficult.
4. GIFMIS Benefits
- Improved budgeting, financial management, and information sharing.
- Provide accurate and up-to-date financial information to the Ghanaian government and its functional entities.
- MDAs and MMDAs reports are generated using a standardised Chart of Accounts and database structure.
- Increased accountability, monitoring, control, and auditing of the federal government's financial operations.
- Coordination of financial control to guarantee that Ministries, Departments, and Agencies (MDAs/MMDAs) spend within their allocated budgets.
- Reduce labor-intensive procedures, effort repetition, and errors.
- Connect distribution to revenue availability in order to increase the efficiency of cash management and treasury management procedures.
- Strengthen relationships amongst financial management organisations such as the Bank of Ghana (BOG), the Public Procurement Authority (PPA), and the Ghana Revenue Authority (GRA).
- Advancing financial laws and ensuring its enforcement.
- Improved information sharing between MDAs/MMDAs and the federal government to facilitate the drafting of reports.
- Ensure accountability by promoting and strengthening internal control mechanisms in public financial management.
- Document business processes, workflows, and approval stages in order to ensure compliance with all MDAs and MMDAs.
- Improved budget preparation, implementation, monitoring, and assessment systems.
- Capability to budget using the chart of accounts, track and monitor projects and funding via the use of the Project.
5. The Governance Structure and Steering Committee for the Project
A Public Financial Management (PFM) Steering Committee was founded in 2010 to offer strategic direction for the project. The Steering Committee is accompanied by an Executive Committee that provides policy direction to the whole project management. Additionally, in December 2012, a Human Resource Management Information System (HRMIS) Steering Committee was formed to assist with the deployment of HRMIS core in 2012.Additionally, the Steering Committee has approved an executive committee to give policy assistance and direction regarding GIFMIS implementation difficulties.
6. Secretariat for the GIFMIS Project
To ease the implementation of the GIFMIS, a Project Secretariat has been established inside the Controller and Accountant General's Department.The Project Secretariat is led by a Project Director, who is aided by two (2) Deputy Project Directors and nine (9) Specialist teams.
Additionally, there is a back-office staff responsible for procurements and financial monitoring of project money.
The GIFMIS Internal Assistance Team (GIST) is a project implementation operational team comprised of Functional Managers, Trainers, Internal Oracle Experts, Advocates, and MDAs Project Implementation Coordinators who provide timely implementation support to users at MDAs and MMDAs.
7. Project Management Team
The Human Resources Management Information System Team, the Budget Team, the Finance and Accounting Team, the Cash management and Treasury Team, the Payroll Team, the Legal Team, the Cultural Change and Process Management Team, the Quality Assurance Team, and the Monitoring and Evaluation Team are the nine (9) expert teams involved in the project's implementation.Each team is comprised of specialists with extensive knowledge in the relevant area. Individual consultants, as well as domestic and international consulting businesses, support some of these teams.
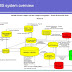
8. Software Description
The Ghana Integrated Financial Management Information System (GIFMIS) is built on the Oracle E Business Suite R12.1.3 platform and includes the following key financial modules:'- Purchasing - for Purchase Orders, Purchase Requisitions, and SRAs
- Accounts Payable — for the purpose of documenting invoices/purchase orders, producing accounting, and managing obligations, including multi-year commitments.
- Cash Management - Managing Bank Accounts, Bank Transfers, Bank Reconciliation, Cash Pooling, and Cash Forecasting, etc.
- Accounts Receivable - for revenue tracking
- Fixed Assets Register - for asset monitoring
9. Scope of GIFMIS
GIFMIS will be implemented in all Ministries, Departments, and Agencies (MDAs) as well as Metropolitan, Municipal, and District Assemblies (MMDAs). The Consolidated Fund, Donor Monies, Statutory Funds, IGFs, and any other public funds are covered by GIFMIS.10. As of 2014, the status of work on GIFMIS implementation
This section discusses procure to pay implementation, network connectivity to outstanding spending units (SUs) in Accra, payroll upgrade and integration, electronic fund transfer (EFT) and Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) and Electronic Bank Reconciliation Swift, as well as the implementation of a business continuity plan (BCP) that includes disaster recovery (DR).- Implementation of Procure to Pay (P2P). As of April 30, all 33 MDAs and ten Regional Treasuries were employing peer-to-peer technology to manage the consolidated fund.
- Network Connection to Accra's Outstanding Spending Units (SUs). As of April 30, 2014, Accra has 230 known SUs, of which 189 had been linked (82 percent ). 41 SUs remained to be linked (which used TPCs to process their transactions). Since October to November 2013, 72 HQ SUs that used the TPCs have been connected to the network.
- Upgrade and integration of payroll. This was accomplished in January 2014, along with the completion of After Production Support. Payroll run for April 2014 finished on the R12 instance.
- Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT), Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications (SWIFT), and Swift Electronic Bank Reconciliation. SWIFT and EFT became operational in October 2013 in all MDAs and in December 2013 in all ten Regional Treasuries. All MDAs and Regional Treasuries operate EFT, although without automated reconciliation.
- Business Continuity Plan (BCP) implementation, including disaster recovery (DR). A technical team has started implementing the suggestions included in the BCP work report. A list of infrastructure needs has been compiled and is being reviewed.
- Ghana Customs Management System (GCMS) The Bank of Ghana (BoG) has conducted a test of its Automated Clearing House (ACH) collection transfer system. The two systems are now connected and exchanging files.
- At the end of February 2014, GRA implemented Accounts Receivable Revenue through Account Receivable.
- Integrating more public money into GIFMIS. Internally Generated Funds (IGF) have made significant progress. In March 2014, two pilot MDAs – the Ministry of Health (MoH) and the Ministry of Education (MoE) – were added to the system (ex-post). Donor Funds: The Ministry of Finance (MoF) and GIFMIS were selected to conduct an ex-ante pilot of the GIFMIS Project.
- Fixed Assets on the GIFMIS platform
11. Budgeting via Program
The Reform is intended to reclassify the budget from activities to programmes and to enhance our budget system's performance reporting. Changes in the following areas are anticipated:- Strengthen the link between government expenditure and intended outcomes.
- Encourage more efficient resource allocation and use.
- Increase the focus on budget information with a policy orientation in order to improve comprehension and discussion in parliament.
- Improve the accuracy of budget data.
- Shifts the focus of budget management away from activities and toward results.
12. Upgrade and Integration of Payroll
• Payroll Upgrade: Improvements were built and pushed out in January 2014, after the completion of Production Support Services, and were utilised to process payroll for April 2014.• Payroll Integration with GIFMIS: A user acceptance test was done, production began in April 2014, and the integrated system was scheduled to be fully implemented in June 2014. The next step was to run a Stress Test utilising GES Payroll Data. However, significant delay was predicted, given the approximately 18 runs necessary and the approximately two weeks required for each run. Additionally, there was a backlog of data to be processed due to the fact that GES had not been run in months and around 89 percent of GES data was resident on the Payroll.
12. TSA - Treasury Single Account
TSA is currently being implemented. The Bank of Ghana (BoG) began calculating interest charges as a TSA (using positive balances in other accounts to offset overdraft in T-Main Account) in January 2014, in compliance with the LFAA.
Source: ir.knust.edu.gh


.webp)






No comments: