Factors Contributing to High Employee Turnover of Lawyers in Law Firms in Kenya
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine the factors contributing to high employee turnover of lawyers in law firms in Kenya.
Methodology: The research design was descriptive survey design. The population of the study was all practicing lawyers based in Nairobi County. The target population is over ten thousand (10,000) lawyers in Nairobi County. The sampling frame was lawyers who are members of LSK. Data was analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) and results were presented in frequency tables. Data was analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) and results presented in frequency tables. The data was then analyzed in terms of descriptive statistics like frequencies, means and percentages.
Results: The study results show that employee turnover was highly emphasized in law firms. The results of the study showed that effects of employee turnover were highly emphasized in law firms. Unique contribution to theory, practice and policy: The study recommended that Management should improve the terms and conditions of services to improve on the employee retention rate so as to avoid liabilities caused by staff turnover and they should provide good working conditions and being transparent and fair to their employee.
Keywords: Employee turnover, lawyers, law firms, retention of employees.
1. BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
Employee turnover is considered to be one of the persisting problems in organizations (Armstrong, 2001; Reiss, 2008), in particular, if it involves quality employees who have worked for the organization for many years, high performers, experienced and loyal individuals (Branham, 2005; Katcher & Snyder; 2007; Somaya & Williamson, 2008). The turnover means that another organization may gain a new knowledge employee who can become its competitive advantage. The loss of knowledge thus is a threat for the former organization, which increases the significance of knowledge continuity.
Mach (2013) noted that Law of course exists in society and for society's needs. It is a man made construct, to facilitate social activities. Law is inconceivable without society. Societies vary greatly and so do legal rules. The largest law firms are found in the United States of America, United Kingdom and Australia (Gray, 2007). One Judge of the Supreme Court of the United States of America and former dean of the Yale Law School once said, "Law feeds and is fed by the world around it. Fortunately, that word is at least as apply described and understood by the humanities as by the social sciences hence, and also, fortunately it is impossible to fully understand law without a deep and sympathetic knowledge of the liberal arts (Yale, 2011).
Law firms must recognize the need to develop policies and practices designed to meet the diverse needs of their legal employees so as to create an environment that encourages them to remain in the employment. Therefore, there is a need to develop an employee retention strategy by looking at the firms' long term goals and what it needs to be successful and have a competitive advantage (Cole, 2002). Good employee relations by the right recruitment will lead into good retention. In this regard law firms invest heavily recruiting of new lawyers and after a few years the lawyers have left the firm. It becomes costly to restart the whole process all over with new lawyers. It becomes a vicious circle with the said attendant costs (Babcock, 2005).
Statement of the Problem
With globalization, which is heightening competition, organizations must continue to develop tangible products and provide services which are based on strategies created by employees. These employees are extremely crucial to the organization since their value to the organization is essentially intangible and not easily replicated (Meaghan & Bontis, (2002). Therefore, managers must recognize that employees are major contributors to the efficient achievement of the organization's success (Abbasi and Hollman, 2000). Managers should control employee turnover for the benefit of the organization success. For instance, staff turnover may impact negatively on the logistics of the law firms by reducing the effectiveness of delivering to the clients.
The problem of this study is that law firms in Kenya and in particular Nairobi County have not fully embraced the importance of the strategic Human Resource Management excellence model of Talent Management so as to give them competitive advantage with other law firms in the country or globally (Kuria et al, 2012). These factors that have led to the high turnover of lawyers as employees need to be identified and addressed. Kyalo (2013) notes that the turnover in the Kenyan legal profession is very high and wonders what can be done to stem it.
Mokaya (2008) did a study on factors that influence labour turnover of aircraft maintenance engineers in Kenya and took a case of Kenya Airways however he did not concentrate on the factors contributing to high employee turnover of lawyers in law firm in Kenya. Njama (2012) did a study on Factors contributing to high employee turnover in CARE Kenya's refugee assistance project in Dadaab- Garissa district however he did not study the factors contributing to high employee turnover of lawyers in law firms in Kenya. However, they did not focus on factors contributing to high employee turnover of lawyers in law firms in Kenya. According to Ramlall (2003), people strive to work and stay in those corporations that provide good and positive work environment, where employees feel that they are valued and making a difference.
All the above studies did not focus on law firms in Kenya. There is therefore a need to investigate high employee turnover of lawyers in law firms in Kenya. This study therefore was intended to fill the gap by assessing factors contributing to high employee turnover of lawyers in law firms in Kenya.
Objective of the Study
The objective of the study was to identify and analyze factors contributing to high employee turnover of lawyers in law firms in Kenya.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
Factors Contributing to Employee Turnover in Law Firms
The State of the Economy and Wages
It is noted that one of the common reasons given by employees exiting is the availability of higher paying jobs. In a better economy the availability of alternative jobs plays a role in turnover. This is the promise of opportunity elsewhere. Employees expect to be fairly compensated for the time and efforts as they work in an organization (Anand, 1997). Wages will indicate what the employer thinks of employee's time and skills are work. Turnover will occur when both the employee and the employer will not be able to agree on the amount of wages to be paid. The literature turnover indicates that successful organizations share a fundamental philosophy of creating value and investing in their employees. Managing turnover of employees is indeed considered a fundamental means of achieving competitive advantage (Maguire, 1995).
Opportunity to Grow/Advancement/Promotion
Employees need room to grow. When there is no opportunity for advancement or promotion employees will look elsewhere for other organizations that will be willing to grow with them. Companies need also to keep in mind that a salary that is enough for a twenty year old might not be enough when that employee reaches in his thirties or forties when he will be required to raise a family (Colling & Terry, 2010).
Work Environment
Generally, lawyers do their work mostly in offices, library and court rooms. However, they can also travel to meetings outside offices e.g. clients' places of business, clients' houses, in prisons or hospitals. They can also be required to appear in legislative bodies/authorities and other places where they travel to gather necessary evidence.
Training and Development
Employees need to have a learning process to acquire knowledge, sharpen their skills, attitudes and behavior so as to enhance their performance. For new hires, the process of mentoring, coaching and on boarding are key to enable them develop the necessary skills, travel, navigate and be engaged into the organizational culture. Here, feedback is also important for both employees and employers. For older employees, the training e.g. in technology is essential in the ever-changing environment (Kisire, 2010).
Effects of Employee Turnover
Monetary Cost
Staff turnover has been noted as one of the most costly problems facing companies. Losing an employee can cost eighteen month's salary for professionals. Therefore, turnover affects the financial position of an organization. The direct cost would be due to recruitment, selection and training of fresh people. This process takes a lot of time and cost. There is also an indirect cost such as workload for the remaining staff and overtime expenses incurred by co-workers. (Hammermesh, 2005).
Client Service
High turnover can harm a business ability to retain clients and provide high quality customer service. Clients may feel comfortable dealing with the same employee over a period of time. Customer loyalty can be built as a result of personal relationships and familiarity. This is particularly true of smaller organizations than the large ones. A trend where employees keep changing may have a negative impact on an organization as it may reflect the inability of the organization to forge lasting working relationships with customers (Kimungu & Mariga).
Productivity
High turnover can result into lower productivity. New employees will often require time to learn on how to fulfill their roles and tasks. It may also negatively impact the remaining workers' morale thus reducing high performance. This will lead to lower productivity and lower profits for an organization. It also results into low morale which in turn will affect organization productivity (Hanel, 2013).
Loss of profit and high quality work for clients
Bureau of Labour Statistics (2008) estimated the cost of employee turnover profit to be up to 150% of employee's remuneration package. These are both direct and indirect costs. Direct costs are leaving costs, replacement costs and transition costs and indirect costs are loss of production, reduced performance levels, unnecessary overtime and low morale.
Burden to Clients and Cost to Individual Lawyer
It is not just law firms that pay the high cost of turnover. Clients share the burden too. They have to learn to establish a new relationship with the new lawyers. This takes time and will compromise client lawyer service relationship which is the bedrock of a firm's reputation and profitability (Abdali, 2011).
3. Improving the Retention of Employees
Knowledge Accessibility
An organization's capacity of making knowledge and ideas widely available to its employees is an advantage. It will make the employees stay longer in the organization. This sharing of information ought to be made available at all levels of management in the entire organization structure. The employees will feel part of the organization, be motivated and the result would be better performance. This will also create a strong organization culture. The employees will feel that they are appreciated by their organization, their efforts are recognized and they will have higher chances of staying in their employment for longer time (Meaghan, 2002).
Work Force Optimization
The organization ought to put into place essential process of getting the desired work done on time and effectively by optimizing the performance of its employees. In addition, the organization is duty bound to provide good working conditions. Moreover, being transparent and fair in its hiring process and establishing accountability would retain employees in an organization (Hunt, 2008).
Mentoring and on Boarding
The starkest reality of surviving in the professional service industry is that competition is severely fierce. There are keen competition and regulatory requirements in all professions, law firms inclusive. Every law firm among other professionals are now expected to be accountable for their time and company's resources. The effect is added workload, e.g. doing more administrative work under greater scrutiny, which leads to pressure and negatively affects employees' moral. In the earlier years, by say twenty (20) years ago, with less pressure then, the mentoring process was effective. A junior employee would be mentored by a partner by treating them like protégés! They would teach, guide the juniors in their career development within the organization. Today, most partners or seniors in large companies are expected to mentor most juniors and their relationships which were one based on covenants have become contractual. It is untenable for such mentoring to be effective (Thomas, Delong, Gabarroad, & Lees, 2008).
Conducting Exit Interviews
An organization should be eager to ask exiting employees why they are leaving. In addition to conducting interviews, the organization can also develop tools like carefully structured questionnaires for existing employees to fill. Whatever information is gathered ought to be used together with other reasons for exit. This is because the existing employees may not disclose full details for fear of victimization as they do not want to burn bridges. Anonymous surveys can also be used as well as conducting self-audits to ascertain certain aspects of job dissatisfaction and exhaustion which will help in selection, hiring or and recruitments (Coleman, 2009).
Career Development Opportunities
A lawyer's career management program that addresses the key issues for turnover will offer a law firm significant savings. It will provide important recruitment interviews beyond compensation and an ongoing support to enhance job satisfaction and higher quality productivity (Rance, 2007).
Policies on Work Life / Balance
The legal profession requires lawyers to work hard to gain position to top law firms in their fields. In most countries, the lawyers find that their needs for work/life balance are secondary. Even in the most educated and ambitious individual consistent long workdays and overwhelming workloads cause employee burnout. The effect of employee turnover is immediately felt in the world of professional services. An existing lawyer almost takes any clients with them. The effect is that the law firms will immediately loose the billable hours or time that the lawyer consistently provided (Mastri, 2007).
Role of Managers as Experts
In the recent years, there has been an evolution in management of law firms. They are hiring nonpracticing lawyers and or highly skilled human resource professionals and firm administrators to support the firm in areas of recruitment, selection, management and development of the professional and non-professional staff. The law firm then works together with the said department to motivate, and retain lawyers. This talented management will turn some departing lawyers into valued alumni rather than a complete loss to the law firm, and further they will provide solid leadership and management intended to achieve desired goals. For it is a said, that for a junior lawyer leaving a law firms are a fact of life. Within reason, that is a sign of a healthy law firm, open to fresh ideas and innovative thinking. But left unchecked, it can reap the heart out of your firm (Mackay, 2004).
Management of Generation Y
The big law firms ought to be encouraged to revise the bill able hour system and become flexible in their hours of working. This is particularly so with the generation Y who are mindful of flexibility in their places of work. They also need a working life balance more than the older generation i.e. the baby boomers. Therefore, the working environment must be looked into. The firms must offer sabbatical leave to employees who have not had enough time off. (Allen, 2004).
3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research design was descriptive survey design. The population of the study was all practicing lawyers based in Nairobi County. The target population is over ten thousand (10,000) lawyers in Nairobi County. The sampling frame was lawyers who are members of LSK. Data was analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) and results were presented in frequency tables. Data was analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) and results presented in frequency tables. The data was then analyzed in terms of descriptive statistics like frequencies, means and percentages.
4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Demographic Characteristics
Gender of Respondents
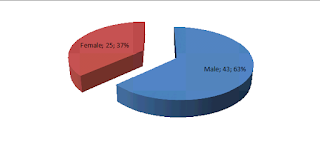
Respondents were asked to indicate their gender. Results on Figure 1 show that 63% of the respondents were males while 37% of the respondents were females. These results are indicative of a male dominated working environment among lawyers in law firms in Kenya.
Age Distribution
Respondents were asked to indicate their age. Based on the analysis presented on Figure 2 majority of the respondents had ages lying between 28 years to 35 years which comprised of 58% of the respondents. Forty six percent (46) of the respondents were lying between ages 36 and above. This implied that most people who work in Kenya's law firms age between 28-35 years which, according to African Youth Charter (2011) is considered to be an age group that defines the youth.
Level of Education
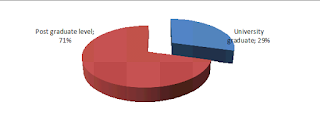
Respondents were asked to indicate their level of education. Based on the results presented on Figure 3 majority (71%) of the respondents were post graduate diplomas and degrees while 29% of the respondents were university graduates. This implies the employees in Kenya's law firms are highly educated as the majority has post graduate degrees. Further implication may indicate that the labor market in the profession of law is highly competitive.
Years in Current Employment
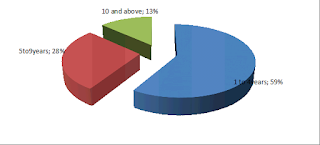
Respondents were asked to indicate the length of experience in their current employment. Figure 5 shows that most of the lawyers had had worked in law firm for a period of between 1 to 4 years. These results show that there is high turnover of lawyers in law firms.
Factors Affecting Turnover
Mean Score of Factors Affecting Turnover
The study sought to determine the factors affecting turnover in law firms in Kenya. The results were presented as follows.
Results indicates that better economy have played a role in turnover and this has been supported by the means score of 3.43 and standard deviation of 0.676. Respondents agreed that most lawyers have structured work schedules and those in law firms in private practice work for long and irregular hours; however, answers on this question varied among respondents as indicated by a mean of 3.31 and a standard deviation of 0.675. Lack of knowledge that sharpens the skills, attitudes and behavior of employee is a factor affecting employee turnover as indicated by the means of 3.26 and standard deviation of 0.661.
Promoting employees is also a factor that can contribute to turn over as supported by a mean of 3.25. Availability of higher paying jobs also was supported by a mean score of 3.25 and a standard deviation of 0.699. Lawyer needs flexible and sustainable jobs as supported by the means of 3.24 and standard deviation of 0.694. Results also indicate that coaching and mentoring is also a factor that affect turnover as supported by the means of 3.22 and standard deviation of 0.666. Further results show that training is a determinant of motivation and agents can sometimes pose a risk to the company through misrepresentation of facts as presented by a mean of 3.91. Result shows that older employees need training in technology as supported by the mean of 3.04 and standard deviation of 0.633. The results indicate that Lawyers are regularly denied promotion and encouraged to look for alternative employment at other firms. The overall mean score of factors affecting turnover is 3.20 and standard deviation of 0.668.
Table 1: Factors Affecting Turnover
Statements
|
Mean
|
Std. Deviation
|
In a better economy, the availability of alternative jobs has played a role in turnover
|
3.43
|
0.676
|
Most lawyers have structured work schedules and those in law firms in private practice work for long and irregular hours
|
3.31
|
0.675
|
If employees lack knowledge that sharpens their skills, attitudes and behavior they exit from employment
|
3.26
|
0.661
|
When there is no opportunity for advancement or promotion employees have looked elsewhere for other organizations willing to grow with them
|
3.25
|
0.583
|
One of the reasons given by employees exiting is the availability of higher paying jobs due to the state of economy
|
3.25
|
0.699
|
Lawyers are leaving the large law firms to go to smaller firms where the work environment is more flexible and sustainable
|
3.24
|
0.694
|
If new hires lack mentoring, coaching which enable them develop the necessary skills, they exit from employment
|
3.22
|
0.666
|
Training is an important determinant of employee motivation and retention in law firms
|
3.07
|
0.63
|
Older employees need training in technology which is essential in the ever changing environment most of them leave employment due to lack of training in technology
|
3.04
|
0.633
|
Lawyers are regularly denied promotion and/or encouraged to look for alternative employment at other firms
|
2.96
|
0.762
|
Total
|
3.203
|
0.668
|
Effect of Turnover
Mean Score Ranking for Effect of Turnover
The study sought to determine the effects of turnover in law firms in Kenya. The results were presented as follows.
Respondents supported that new employees will often require time to learn on how to fulfill their roles and tasks as represented by a mean of 3.15. Results show that turnover lowers productivity in organizations because it reduces on the efficiency of operations as supported by a mean of 3.13. Respondents agreed that turnover negatively impact the remaining workers' morale thus reducing high performance as indicated by a mean of 310 and standard deviation of 0.60. Respondents agreed that whenever staffs leave an organization, services rendered to customers are interfered with as supported by 3.09.
Result indicates that organization incurs high direct cost due to recruitment and training of fresh people as supported by 3.09. Respondents agreed that turnover affects image of organization negatively as supported by a means of 3.07. Results indicates that the slow rate of service to customers lowers customer satisfaction levels and thus spoils the reputation of the organization as supported by a means of 3.07. Changes in employees has reflected inability to forge lasting working relationships with customers is a factor affecting turnover as indicated by the means of 3.07. Respondents agreed that turnover affects the financial position of our organization as supported by the mean of 3.04. Results also indicate that departure of one employee greatly affects the output of the whole organization as it affects the processes as supported by a mean of 3.03.
Further results show that a trend where employees keep changing had a negative impact on their organization as supported by a mean of 3.03. Results also show that Long-term employees generally have higher productivity and efficiency on the job than newer employees, due to their length of experience with the firm as supported by a mean of 3.00. Respondents also agreed that Customers are not attended to in time due to shortage of staff and this is supported by the mean of 3.00. It was also confirmed that loyal employees also improve operational processes and train incoming employees as indicated by a mean of 2.96.
Result shows that Clients feel comfortable dealing with the same employee over a period of time as supported by a mean of 2.94. It was confirmed that there is an indirect cost in our organization such as workload for the remaining staff and overtime expenses incurred by co-workers as indicated by a mean of 2.93. Result indicates that High turnover has harmed our business ability to retain clients and provide high quality customer service as supported by mean of 2.91. The overall mean score of effects of turnover is 3.04 and a standard deviation of 11.85.
Table 2: Effect of Turnover
Statements
|
Me an
|
Std.
Deviat ion
|
New employees will often require time to learn on how to fulfill their roles and tasks
|
3.15
|
0.61
|
Turnover lowers productivity in organizations because it reduces on the efficiency of operations
|
3.13
|
0.54
|
High turnover can result into lower productivity
|
3.13
|
0.64
|
Turnover may also negatively impact the remaining workers' morale thus reducing high performance
|
3.10
|
0.60
|
Whenever staffs leave an organization, services rendered to customers are interfered with.
|
3.09
|
0.69
|
Our organization incurs high direct cost is due to recruitment, selection and training of fresh people
|
3.09
|
0.64
|
Turnover affects image of our organization negatively
|
3.07
|
0.70
|
The slow rate of service to customers lowers customer satisfaction levels and thus spoils the reputation of the organization
|
3.07
|
0.56
|
Changes in employees has reflected inability to forge lasting working relationships with customers
|
3.07
|
0.70
|
Turnover affects the financial position of our organization
|
3.04
|
0.68
|
Departure of one employee greatly affects the output of the whole organization as it affects the processes
|
3.03
|
0.65
|
A trend where employees keep changing had a negative impact on our organization.
|
3.03
|
0.73
|
Long-term employees generally have higher productivity and efficiency on the job than newer employees, due to their length of experience with the firm
|
3.00
|
0.63
|
Customers are not attended to in time due to shortage of staff
|
3.00
|
0.60
|
Loyal employees also improve operational processes and train incoming employees
|
2.96
|
0.70
|
Our Clients feel comfortable dealing with the same employee over a period of time.
|
2.94
|
0.73
|
There is an indirect cost in our organization such as workload for the remaining staff and overtime expenses incurred by co-workers
|
2.93
|
0.74
|
High turnover has harmed our business ability to retain clients and provide high quality customer service
|
2.91
|
0.73
|
Total
|
3.04
|
11.85
|
Improving the Retention of Employees
Mean Score Ranking for Improving the Retention of Employees
The study sought to determine the suggestion for improving the retention of employees in law firms in Kenya. The results were presented as follows.
Results indicates that sharing of information should to be made available at all levels of management in the entire organization structure and this has been supported by the means score of 3.09. Respondents agreed that their organization need to mentor the juniors in their career development as indicated by a mean of 3.07. Clarity should be increased in the workplace as most of the respondents agreed as indicated by the means of 3.03. Results also indicated that lawyers are eager to discuss career growth issues and therefore law firms should facilitate this and it was supported by a mean of 3.01. Further result indicates that being transparent and fair in its hiring process and establishing accountability would retain employees in an organization as supported by the means of 3.01.
Results also indicate that sharing with employees will make them feel that they are appreciated by their organization as supported by the means of 3.00. Further results show that organization should be eager to ask exiting employees why they are leaving as presented by a mean of 2.99. Result shows that the organization need to focus on new and more effective ways to improve employee efficiency, training, and retention to ensure a more engaged workforce as supported by the mean of 2.97. The results indicate that supervision should be improved to reduce turn over as indicated by a mean of 2.97.
It was also confirmed that sharing with employees will make them feel that their efforts are recognized and they will have higher chances of staying in their employment for longer time as it was supported by a mean of 2.97. Findings also indicated that law firms need to adjust the working hours and offer a flexible environment especially with the new age of technology which offers options for one to work from outside the office as it was supported by a mean of 2.97. Result also indicates that their organization should be duty bound to provide good working conditions as supported by a mean of 2.96. The overall mean score for improving retention of employee is 3.00 and standard deviation of 0.60.
Table 3: Improving the Retention of Employees
Statements
|
Mean
|
Std. Dev.
|
Sharing of information should to be made available at all levels of management in the entire organization structure
|
3.09
|
0.59
|
Our Organization need to mentor the juniors in their career development
|
3.07
|
0.63
|
Clarity should be increased in the workplace
|
3.03
|
0.69
|
Lawyers are eager to discuss career growth issues and therefore law firms should facilitate this
|
3.01
|
0.61
|
Being transparent and fair in its hiring process and establishing accountability would retain employees in an organization
|
3.01
|
0.53
|
Sharing with employees will make them feel that they are appreciated by their organization
|
3.00
|
0.57
|
Our organization should be eager to ask exiting employees why they are leaving
|
2.99
|
0.66
|
The organization need to focus on new and more effective ways to improve employee efficiency, training, and retention to ensure a more engaged workforce
|
2.97
|
0.52
|
Supervision should be improved to reduce turn over
|
2.97
|
0.65
|
Sharing with employees will make them feel that their efforts are recognized and they will have higher chances of staying in their employment for longer time
|
2.97
|
0.65
|
Law firms need to adjust the working hours and offer a conducive flexible environment especially with the new age of technology which offers options for one to work from outside the office
|
2.97
|
0.62
|
Our organization should introduce on boarding programs designed to ensure that newly hired employees are quickly and effectively integrated into the work place
|
2.96
|
0.63
|
Our organization should be duty bound to provide good working conditions
|
2.96
|
0.80
|
Total
|
3.00
|
0.63
|
5. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Summary of Findings
Factors Contributing to High Employee Turnover of Lawyers in Legal Firms
One of the objectives of the study was to determine the factors contributing to high employee turnover of lawyers in legal firms. Results indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that one of the reasons given by employees exiting is the availability of higher paying jobs due to the state of economy.
Results revealed that majority of the respondents agreed with the statement that in a better economy the availability of alternative jobs have played a role in turnover. The findings agree with those in Schaefer (2010) that turnover at law firms has always been higher given the up-or-out nature of the law firms when the economy is not doing well. The study started with biographies of over one thousand lawyers of the said two hundred and eighty five largest American law firms and matched data of the turnover based on the three categories. The findings show the firm- specific human capital and/or skills that are specific to large firms are important at these firms.
Furthermore, the findings indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that when there is no opportunity for advancement or promotion employees have looked elsewhere for other organizations willing to grow with them. The study findings also revealed that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that Lawyers are regularly denied promotion and/or encouraged to look for alternative employment at other firms In addition, the study findings indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statement that most lawyers have structured work schedules and those in law firms in private practice work for long and irregular hours.
The findings agree with those in Alan, 2009 and Garicano, 2007 who conducted the study of the American law firms aforesaid, the finding was that given the up and out nature of law firms, lawyers are regularly denied promotion and/or encouraged to look for alternative employment at other firms. The research further noted that large law firms are transient institutions with many of the lawyers working there leaving within a few years of arriving. The turnover at these firms has been more drastic recently due to layoffs brought about by the decline of demand of legal services. Moreover, it was noted that the rate of turnover dropped drastically with experience. There is also a correlation of turnover to school based lawyer networks, gender and law school prestige. American law firms pay their employees according to the working hours they are able to perform. The system considers payment through the amount of output produced by the employee.
The study findings also revealed that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that Lawyers are leaving the large law firms to go to smaller firms where the work environment is more flexible and sustainable and if employees lack knowledge that sharpens their skills, attitudes and behavior they exit from employment In addition, the study findings indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statement that If new hires lack mentoring, coaching which enable them develop the necessary skills, they exit from employment.
The findings agree with those in previous research Samganakkan, 2010; Kevin et al., 2004; Elias, 1994; which suggests that research training is an important determinant of employee motivation and retention and compensation should be such which force the employees to stay in the organization as retention is an important matter for the organizations effectiveness. For a company to become a good employer and also to succeed, it is important that they keep their turnover rate low and for this purpose compensation is one of the important things to keep employees motivated and retained.
Finally, results indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that Older employees need training in technology which is essential in the ever changing environment most of them leave employment due to lack of training in technology and training is an important determinant of employee motivation and retention in law firms. The findings agree with those in Kisire, 2010; Kaufman and Hotchkiss, 2006; which noted that Employees need to have a learning process to acquire knowledge, sharpen their skills, attitudes and behavior so as to enhance their performance. For new hires, the process of mentoring, coaching and on boarding are key to enable them develop the necessary skills, travel, navigate and be engaged into the organizational culture. Here, feedback is also important for both employees and employers. For older employees the training e.g. in technology is essential in the ever changing environment.
Effects of Employee Turnover
The other objective of the study was to determine the effects of employee turnover in legal firms. Results indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that turnover affects image of their organization negatively. Results also revealed that majority of the respondents agreed with the statement that turnover affects the financial position of their organization, their organization incurs high direct cost is due to recruitment, selection and training of fresh people; there is an indirect cost in our organization such as workload for the remaining staff and overtime expenses incurred by co-workers. The findings agree with those of Price et al. (1997) who found that employee turnover has a significant effect on the financial performance of an organization.
Furthermore, the study findings indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that high turnover has harmed their business ability to retain clients and provide high quality customer service, their clients feel comfortable dealing with the same employee over a period of time and a trend where employees keep changing had a negative impact on our organization. The findings further agree with those in Kimungu and Mariga, (2009) who found that high turnover can harm a business ability to retain clients and provide high quality customer service. Clients may feel comfortable dealing with the same employee over a period of time. Customer loyalty can be build as a result of personal relationships and familiarity. This is particularly true of smaller organizations than the large ones. They found that a trend where employees keep changing may have a negative impact on an organization as it may reflect the inability of the organization to forge lasting working relationships with customers.
Results indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that changes in employees has reflected inability to forge lasting working relationships with customers, whenever staffs leave an organization, services rendered to customers are interfered with. Customers are not attended to in time due to shortage of staff, the slow rate of service to customer's lowers customer satisfaction levels and thus spoils the reputation of the organization and high turnover can result into lower productivity.
Lashley (2009) found that new employees would need time to adapt to the new environment and to internalize the establishments' service standards. In most cases, this slowed down service delivery and that for an establishment to be competitive there must be a stable labour force. The findings also agree with those of Tyson and Fell (2010) who observe that in the event that one staff leaves the organization, customers are among the first to know that work is not being done well. In some cases, those who take the jobs of those who have exited are not so efficient, or not so familiar with the procedures. The slow rate of service to customers lowers customer satisfaction levels and thus spoils the reputation of the organization.
Finally, results indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that new employees will often require time to learn on how to fulfill their roles and tasks, turnover may also negatively impact the remaining workers morale thus reducing high performance, turnover lowers productivity in organizations because it reduces on the efficiency of operations, departure of one employee greatly affects the output of the whole organization as it affects the processes, Long term employees generally have higher productivity and efficiency on the job than newer employees, due to their length of experience with the firm and Loyal employees also improve operational processes and train incoming employees. The findings agree with those of Armstrong (2001) who observed that long-term employees generally have higher productivity and efficiency on the job than newer employees, due to their length of experience with the firm he also found that loyal employees improve operational processes and train incoming employees.
Improving the Retention of Employees
The other objective of the study was to determine how law firms improve the retention of employees in legal firm. Results indicated that majority of the respondents agreed with the statements that sharing of information should be made available at all levels of management in the entire organization structure, sharing with employees will make them feel that their efforts are recognized and they will have higher chances of staying in their employment for longer time, sharing with employees will make them feel that they are appreciated by their organization, supervision should be improved to reduce turn over, clarity should be increased in the workplace and our organization should be duty bound to provide good working conditions. The findings agree with those of Howatt (2004) who noted that Employees will leave jobs due to personality conflicts.
The number one reason employees leave is not money; it is conflict with their direct supervisor. Most personality conflicts are rooted in poor communication and a lack of communication skills focused on achieving agreement. He noted that clarity should be increased in the workplace. The business is a living process, and it is not good enough to adhere to a static set of goals; employees need to know the day-to-day changes in direction. It is important that employees have a process where they are obtaining clarity on a daily basis.
In addition, the study findings indicated that majority of the respondents strongly agreed with the statement that being transparent and fair in its hiring process and establishing accountability would retain employees in an organization, the organization need to focus on new and more effective ways to improve employee efficiency, training, and retention to ensure a more engaged workforce, Our Organization need to mentor the juniors in their career development, Our organization should introduce on boarding programs designed to ensure that newly hired employees are quickly and effectively integrated into the work place and Our organization should be eager to ask exiting employees why they are leaving.
The result concur with those of Jabra (2011) who noted that when it comes to job satisfaction, Contact Center employees are clear that they want more than just good working conditions. They want to have input and influence on their working environment and the right equipment for the job. They also want jobs that are rewarding and challenging, opportunities for advancement within the organization and career fulfillment. They also appreciate public recognition for their contributions. In short, Contact Center employees want to be part of a dynamic, successful organization.
Finally, results revealed that majority of the respondents agreed with the statement that Lawyers are eager to discuss career growth issues and therefore law firms should facilitate this and Law firms need to adjust the working hours and offer a conducive flexible environment especially with the new age of technology which offers options for one to work from outside the office.
Conclusions
The study concludes that employee turnover was highly emphasized in law firms. The results of the study make it possible to conclude that effects of employee turnover were highly emphasized in law firms. It was also concluded that improving employee retention can improve law firm in Kenya.
Recommendations
The study recommended that Management improve the terms and conditions of services so as to improve on the employee retention rate so as to avoid liabilities caused by staff turnover and they should provide good working conditions and being transparent and fair to their employee.
Interested in more articles on employee turnover? Please Click [here].
You Might Also Like:
Effect
of health and safety on employee performance pdf
Disclaimer: This article was published under the Creative Commons License.
How to Cite this Article:
Maangi, J. K., & Wambalaba, F. (2017). Factors contributing to hign employee turnover of lawyers in law firms in Kenya. Journal of Modern Law and Policy, 1(1), 1–21
REFERENCES
Armstrong, M. (2001). A handbook of Human Resource Management and Practice, 8th Edition. Bath Press Ltd.
Babcock P. (2005). Find What Workers Want, H.R. Magazine, April, ww.shrm.org/hrmagazine Branham, L. (2005). The 7 hidden reasons employees leave. New York: AMACOM.
Cole G.A. (2002). Personnel and Human Resource Management, 5th Edition. Biddles Ltd,
Guildford and Kings Lynn
Colling, T. & Terry, M. (2010). Work, the employment relationship and the field of Industrial relations. Theory and practice. 3rd ed. West Sussex: Wiley.
Gray, J. T. (2007). Restructuring law firms: Reflexivity and emerging forms, in Brock, D., Powell, M. and Hinings, C. R.(eds) Restructuring the professional organization, London. Routledge, 87-104.
Hammermesh, D. (2005). Labour demand and the structure of adjustment costs, Economic Journal, 105, 620-34.
Katcher, B. L., & Snyder, A. (2007). 30 reasons employees hate the in managers. New York:
AMACOM.
Kimungu,S. I., & Mariga, P. M (2010). An assessment of the impact of employee turnover on customer service and competitiveness of an establishment. International Research Symposium in Service Management, ISSN 1694-0938
Kisire, S. J. (2010). Human Resources Management "Simple Revision Guide. Nairobi: Printed By Bernard Bonyo.
Kuria.S., Wanderi P., & Ondigi, A., (2011). Factors influencing labour turnover in three and five scar-rated hotels in Nairobi, Kenya. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science 1(20)
Mach, K. W. (2013). Representing the Race. Harvard Law Review, 126 (330). Retrieved from http://www.humanrights.org/wp-content/upload/2012/05/jhrpd.
Mackay, K. (2004). The National Phonex Legal. Canadian Bar Asssociation. doi: www.phonexlegal.com/documents/articles/managment
Maguire, M. (1995). Men, Women, Passion and Power. London: Routledge
Mastri A. I. (2007). The effect of work/life balance policies on employee retention and profitability. A dissertation submitted to the school of education and the committee on graduate studies of Stanford University
Meaghan, S. & Bontis, N. (2002). Voluntary turnover: knowledge management-friend or foe J.
intellect. 3 (3): 303-322
Mokaya, S. O. & Kittony, L.K. (2008) Factors that Influence Labour Turnover of Aircraft Maintenance Engineers in Kenya: A Case of Kenya Airways.
Njama, K. (2012) Factors contributing to high employee turnover in CARE Kenya's refugee assistance project in Dadaab- Garissa district. Unpublished KU thesis
Ramlall, S. (2003). Organizational Application Managing Employee Retention as a Strategy for Increasing Organizational Competitiveness, Applied H.R.M. Research, 8(2), 63-72.
Reiss, C.H. (2008). [E-text type]. Retrieved from http://www.personaler-online de/typo3/nc/personalthemen/suche-in-artikeln/detailansicht/artikel/fluktuation.html.
Somaya, D. & Wolliamson, I.O. (2008). Rethinking the "War for Talent". MIT Sloan Management Review, 29-34.
Thomas, D. J. (2008). Mentoring matters in the Hypercompetitive World. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved /Oct /22nd, /2013
Yale, A. (2011). Law School. Cambridge Press. Retrieved from
http://www.law.yale.edu/about/adminstrative offices.html


.webp)






No comments: