Anuria - Definitions, Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Description
Anuria is a condition where there is a little amount of urine discharge from the body. The main cause of anuria includes severe kidney problems, hypovolemia, cardiogenic shock, and sepsis. The term "anuria" indicates absence of urine. In most cases of anuria patients, the urine production would be in the very low level. If untreated, anuria can cause death. Kidneys would not stop urine production but would be able to produce in low quantity.
Causes
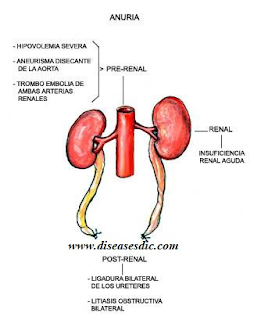
The causes of Anuria is broadly categorized into Pre-renal Cause, Renal cause and Post renal Cause.
Pre-Renal Causes:
There are problems outside the kidneys that can lower the urine production. These factors are included in the pre-renal causes. The problem occurring in the areas of blood vessels before it reaches the kidneys are also referred to as pre-renal causes. The major pre-renal causes are as follows;
- Hypovolemia conditions like blood leakage (hemorrhage)
- Low systemic vascular resistance can occur due to severe sepsis
- Low systemic vascular resistance can occur due to severe sepsis
- Other causes include pancreatitis, sudden compression of renal vein or inferior vena cava, a sudden increase in abdominal pressure, sudden increase of blood sugar levels
Renal cause:
- The problems that occur in the kidneys are grouped as "renal origin". Presence of glomerulus and renal tubules can drastically reduce urine output causing anuria.
- Autoimmune diseases, glomerulonephritis, certain kinds of nephrotoxic drugs like amphotericin B, powerful diuretics, ACE inhibitors, kidney diseases acquired by birth (congenital), and hematuria can cause anuria.
Postrenal Cause:
- Postrenal causes occur with the outflow of urine from the kidneys. Obstruction causes in the kidneys can include a mass, calculi, lower urinary tract issues.
- Prostatic hypertrophy, stenosis, bilateral ureteral block, problems in the posterior urethral valves and kinks in the catheter can cause anuria.
Risk factors
- People with congenital kidney problems
- People with recurrent urinary tract infection
- People with enlargement of prostate glands
- People who have recently undergone renal surgery are at risk of anuria.
Symptoms
Anuria or not urinating is a symptom itself and not a medical condition. Sometimes, a person may also have signs of the condition that is causing the poor urine output.
The symptoms of kidney disease can include:
- Swelling in the legs, feet, ankles, face
- Rash or itching of the skin
- Flank pain in the back or side
- Nausea or vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Fatigue
Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis include:
- Excessive thirst
- Dry mouth
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- Fruity odor on the breath
Complications
- Cardiovascular abnormalities can affect the fluid and sodium retention processes of the body, presenting as anuria.
- Gastrointestinal problems leading to severe vomiting or diarrhea can lead to extreme dehydration and imbalances in volume status.
- Hematological issues such as anemia or platelet dysfunction are also potential complications.
- Electrolytes of the body that normally get excreted by the kidneys may also cause complications, as substances such as potassium can start to build up, leading to an overabundance.
- Hyperkalemia, an increased amount of potassium in the system can lead to kidney damage, cardiac arrhythmias, and other ECG abnormalities.
Diagnosis and Test
When diagnosing anuria, your doctor will first ask you questions about the symptoms you may be having. These include questions about urine retention, recent trouble urinating, fatigue, or having blood in your urine.
If your doctor suspects you have anuria, a closer look at kidney function will be initiated. This could include ordering the following tests:
- Urinalysis – A urinalysis is a laboratory test. It can help your doctor detect problems with your body that may be indicated by your urine. The doctor will do a microscopic exam, Dipstick test, and Visual exam to examine your urine.
- CT scan – CT scan or CAT scan) is a noninvasive diagnostic imaging procedure. CT scans of the kidneys are useful in the examination of one or both of the kidneys to detect conditions such as tumors or other lesions, obstructive conditions, such as kidney stones, congenital anomalies, polycystic kidney disease, accumulation of fluid around the kidneys, and the location of abscesses.
- MRI scan – A kidney MRI can be used to guide doctors or surgeons during a procedure, such as a biopsy. An MRI scan may be used if surgery is needed to remove a growth or lump.
- Renal scintigraphy – Renal scintigraphy uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiopharmaceuticals, a special camera, and a computer to evaluate your kidneys' function and anatomy and determine whether they are working properly. It can provide unique information that is often unattainable using other imaging procedures.
- Needle biopsy. After an anesthetic is given, the health care provider inserts the biopsy needle into the kidney to get a sample. Ultrasound or computerized tomography (CT scan) may be used to guide the needle.
- Open biopsy. After an anesthetic is given, the health care provider makes an incision in the skin and surgically removes a piece of the kidney.
Treatment and Medications
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Fluid resuscitation of 250-500 mL aliquots may be the key in order to increase urine output and stabilize heart rate and blood pressure. The goal is for the patient to have a urine output of at least 0.5 mL/kg/hr. Central venous pressure is maintained at 8-12 mmHg via the central venous catheter. Blood pressure is very accurately measured through an arterial line. If the fluid challenge fails, inotropes come to the rescue.
Nephrotoxic drugs
If the patient is taking drugs that are toxic to the kidneys (as noted above), discontinue these medications. It is also important to release the obstruction, decrease intra-abdominal pressure, and treat the underlying infection.
Diabetes management
People with diabetes should be careful to control their blood sugar levels. It is important to monitor blood sugar as directed, follow the prescribed diet and exercise regimen, and to take all medication, as directed.
Lifestyle changes
Making positive lifestyle changes is also very important for someone with high blood pressure. The doctor should recommend diet and exercise changes and may suggest medication to help keep blood pressure low. Stress relief and getting enough sleep are also necessary.
Removing kidney stones or tumors
Someone with an obstruction in the kidneys, such as from a kidney stone or tumor, will need to have it removed. This may mean surgery, medication chemotherapy, or radiation therapy to shrink or remove the tumor or stone.
Home or Natural Remedies
- Cucumber: Combine one teaspoon of ground cucumber seeds and one glass of coconut water.
- Avocado: Boil 500 milligrams of water and add 200 grams of avocado leaves. Leave it overnight. Drink one cup of mixture daily.
- Cabbage: Use daily in broths, soups, or salads.
- Java Tea: Boil one cup of water with five grams of java tea leaves twice daily.
- Chayote: Boil one cup of water with the leaves or seeds of chayote for a drink to be taken twice daily.
- Carrot: Mix four grams of carrot seed with one glass of warm water for a drink to be taken three times a day.
- Land Caltrops: Boil one plant and add one teaspoon of honey to every 20 milligrams of the mixture for a daily drink.
Outlook
- Even after increased water intakes, no improvement is found in the urination
- In case of diarrhea if vomiting or a feeling of nausea, lightheadedness, fever, dizziness or fat pulse is observed.



.webp)






No comments: